NEWS & KNOWLEDGE
What is infertility?

What is Infertility?
Infertility is the inability to conceive after 12 months of regular, unprotected intercourse. It can be caused by abnormalities in either women or men. Many people may not even be aware that they have this condition. The risk of infertility increases with age, particularly in women who are 35 years or older.
How Can I Know If I Have Infertility?
You can start with a basic self-evaluation. Infertility may be suspected if a couple has been trying to conceive for one year, having regular sexual intercourse 2–3 times per week without using any form of birth control, but pregnancy has not occurred.

Causes of Infertility
In Women:
Infertility may be caused by:
-
Problems with ovulation, such as irregular or absent ovulation.
-
Premature ovarian insufficiency (early depletion of ovarian hormones).
-
Irregular or absent menstruation.
-
Blocked or damaged fallopian tubes.
-
Previous surgery on the uterus or ovaries that affects fertility.
In Men:
Infertility may be caused by:
-
Poor semen quality or low sperm count.
-
Reduced sperm motility (low movement ability).
-
Problems with ejaculation.
-
Hormonal disorders affecting sperm production.
-
Congenital conditions affecting reproductive function.
What Methods Can Detect Infertility?
The first step is for both partners to consult a doctor. The doctor will begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination.
Medical history may include:
-
Past surgeries, especially those involving the reproductive organs.
-
For women: menstrual history and ovulation patterns.
-
Lifestyle factors for both partners, such as alcohol consumption, smoking, and daily habits, which can affect fertility.
After reviewing the medical history, the doctor will perform a physical examination for both men and women to identify any potential issues that may contribute to infertility.
Diagnostic Methods for Infertility
For Women:
-
Ultrasound examination: To evaluate the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries for any abnormalities.
-
Ovarian hormone testing: Including AMH (Anti-Müllerian Hormone) to assess ovarian reserve and function.
For Men:
-
Semen analysis: To evaluate sperm count, motility, morphology, and overall semen quality.
-
If semen quality is below the standard, the doctor may perform additional physical examinations to identify possible underlying causes.

Does the Examination Take a Long Time?
The basic examination, including medical history and physical examination, takes approximately 1 hour. If additional tests, such as blood tests or semen analysis, are required, the total time may be around 2–3 hours.
Preventing Infertility
Preventing infertility completely can be challenging, as it can result from many factors. These may include lifestyle habits, such as insufficient sleep, poor nutrition, exposure to harmful chemicals, or medical treatments like chemotherapy.
Although not all causes of infertility can be avoided, you can reduce the risk by taking care of your health:
-
Get adequate sleep.
-
Eat a nutritious, high-protein diet.
-
Exercise regularly.
-
Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins whenever possible.
Medical Technology Treatment Guidelines
If a couple does not have significant fertility problems, the doctor may recommend:
-
Monitoring ovulation and timing sexual intercourse accordingly.
-
Ovulation-stimulating medications to help eggs mature.
-
Ultrasound examinations to monitor egg growth and determine the optimal day for ovulation.
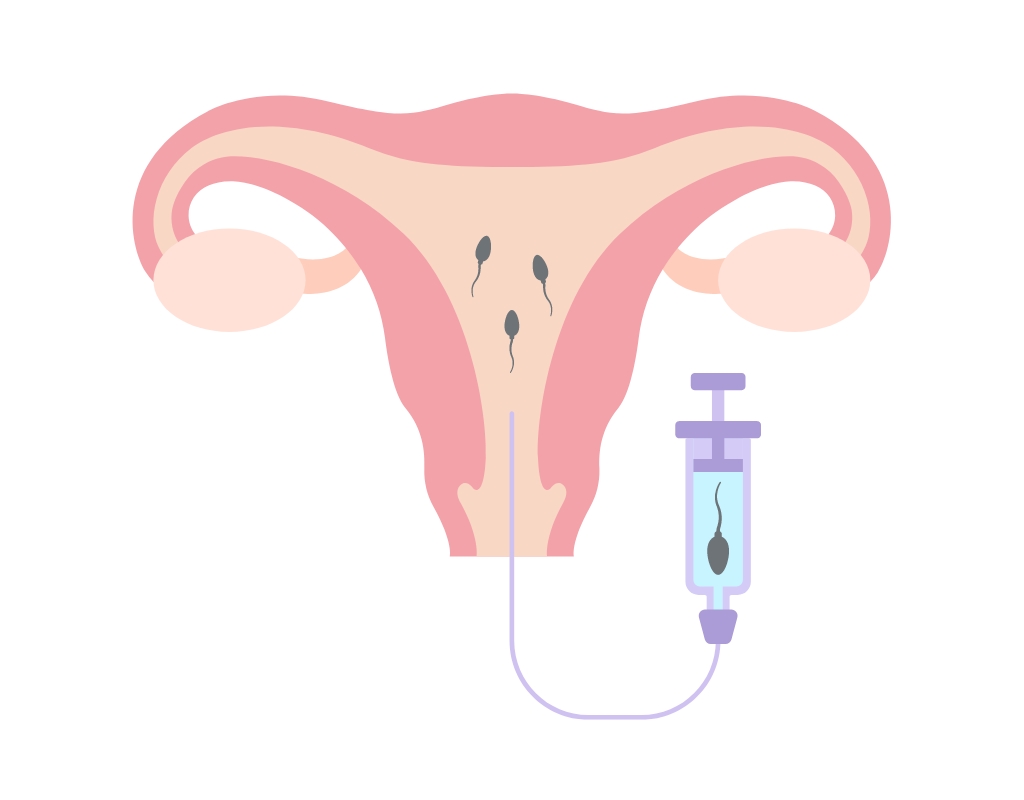
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a procedure in which sperm is carefully prepared in the laboratory to remove impurities and select the healthiest, most motile sperm. The prepared sperm is then directly inserted into the uterus on the day the woman ovulates.
IUI is typically suitable for couples with mild infertility, such as:
-
Women with normal uterine cavities and open fallopian tubes.
-
Men with medium to good semen quality.
This method is less invasive and often used as a first-line treatment before more advanced assisted reproductive technologies like IVF.
IVF/ICSI (In Vitro Fertilization / Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) begins with stimulating the ovaries to produce multiple eggs using medications tailored to each patient. Once the eggs mature, they are retrieved from the woman, and sperm is collected from the man. The healthiest sperm are then selected and combined with the eggs in the laboratory to achieve fertilization. The resulting embryos are cultured until they develop and are ready for transfer.
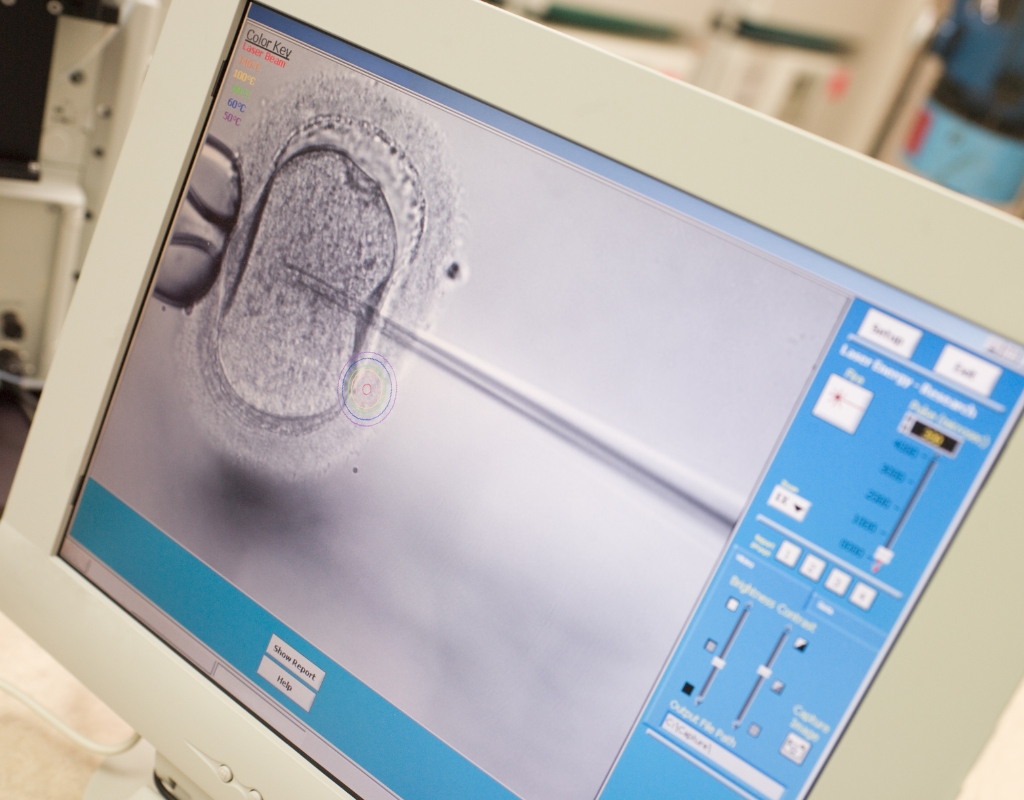
ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) is a specialized IVF technique in which a single sperm is directly injected into an egg to facilitate fertilization. ICSI is used in cases where:
-
The sperm cannot penetrate the egg naturally.
-
The egg has a particularly thick outer layer (zona pellucida) that prevents fertilization.
After fertilization, embryos are cultured in the lab until they reach the blastocyst stage (usually Day 5), which is the optimal stage for implantation into the uterus.
The doctor will consider the patient’s medical history, ovarian function, and hormone levels. Based on this evaluation, the doctor will select the treatment method most appropriate for each individual patient.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert


