NEWS & KNOWLEDGE
Oocyte Freezing

Oocyte Freezing
In modern Thai society, there is a growing trend of marrying at an older age. As is well known, maternal age has a direct impact on the quality of a woman’s eggs. As illustrated in Figure 1, the most fertile age range is between 25 and 29 years. After this period, fertility gradually declines, with a marked decrease occurring after the age of 35. This decline in fertility forms the basis for the recommendation to consider egg freezing before the age of 35. Egg freezing preserves the age and quality of the eggs at the time of retrieval, thereby preventing further deterioration as the woman ages.
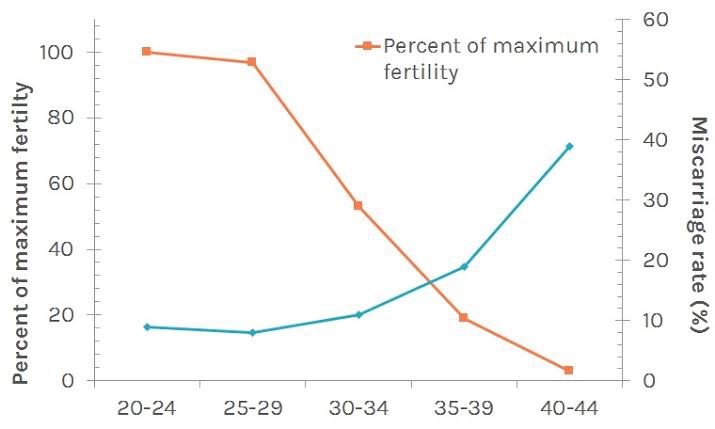
Picture 1 shows the relationship between age range and fertility percentage.
Additionally, eggs from women over 35 years of age are more likely to result in embryos with chromosomal abnormalities when fertilized with sperm. This is illustrated in Figure 2.
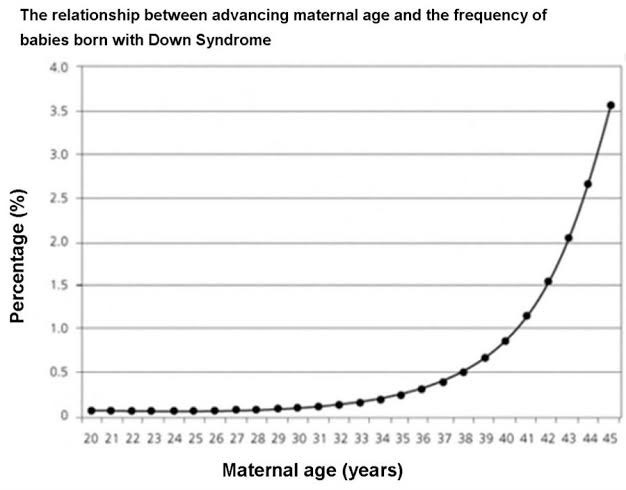
Picture 2 demonstrates the relationship between age of women and percentile of having Down syndrome babies.
Moreover, a woman’s egg supply is determined before birth, with the highest number of eggs present at around seven months of gestation. From that point onward, the number of eggs gradually declines over time. This natural age-related decline is the reason why it is advisable to consider egg freezing at a younger age, as illustrated in Figure 3.
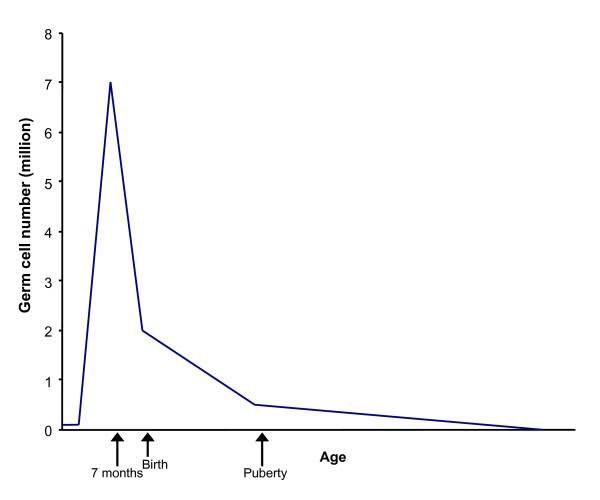
Picture 3 demonstrates egg production and ages of women (Puberty)
Oocyte Freezing Process
The process of oocyte freezing involves stimulating the ovaries with hormone injections, following a protocol similar to that used in in vitro fertilization (IVF), to retrieve a sufficient number of mature eggs. Once the eggs have reached the appropriate stage of maturity, they are collected from the body and frozen prior to fertilization with sperm.
The freezing technique is essentially the same as that used for embryo cryopreservation, with the primary difference being the type of cryoprotective agents employed. However, frozen oocytes tend to be less robust than frozen embryos. Upon thawing for fertilization, approximately 80% of the frozen eggs are expected to survive the process.
Indications for Oocyte Freezing
-
Elective egg freezing: For the purpose of future fertilization with a legally married partner’s sperm.
-
Medical egg freezing: For women diagnosed with certain cancers who will undergo treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or surgery that may impair ovarian function. Egg freezing may also be considered for other medical conditions where treatment is expected to adversely affect the quantity or quality of oocytes in the future.
By Assoc.Prof. Matchuporn Sukprasert